Product Overview
The high-quality, versatile binder VG Grade Bitumen is primarily used for road construction and industrial tasks. Consistency across various climatic conditions and construction requirements is ensured by the classification of VG Grade Bitumen. For projects demanding reliable and long-lasting results, VG Grade Bitumen is an ideal choice.
Applications
VG Grade Bitumen is extensively used in:
• Ensures the creation of durable, high-quality asphalt pavements for highways, urban roads, and rural pathways.
• Heavy aircraft loads and varying weather conditions can be a challenge for airport runways.
• A durable and resistant surface for industrial floors guards against damage from heavy machinery.
• Waterproofing is used in waterproofing applications for buildings and structures to prevent water ingress and damage.
• Weatherproofing and durability are provided by the roofing component in roofing felt and shingles.
Advantages of Viscosity Grade Bitumen
• Quality and performance are ensured across various climatic conditions and traffic loads.
• It is cost-effective and provides a long-lasting solution for construction and industrial projects.
• The straightforward and efficient application reduces time and labor expenses.
• UV radiation, moisture, and temperature swings are some of the environmental factors that make it tough.
• The performance of VG Grade Bitumen can be affected by extreme conditions.
• Regular maintenance is needed to ensure longevity and optimal performance of bitumen surfaces.
• Responsible handling and disposal are required for the production and application of bitumen.
VG 10
Viscosity grade bitumen (asphalt) is known to be a suitable paving grade bitumen for road construction and for the production of pavement asphalts with controlled properties.
Bitumen Grade VG 10 from the ABM-Petro group is a standard viscosity grade Bitumen usually used as a paving Bitumen suitable for road construction and other industrial purposes. Hot mix asphalt for bases and wearing courses is manufactured using this grade of bitumen.
Typical properties of Bitumen VG 10
ABM-Petro group guarantees that the Bitumen Grade VG 10 it supplies under its offers is produced in compliance to and is in conformity to IS 73:2006 and meets the following specification requirements.

Applications
Bitumen VG-10 is most commonly utilized in spraying usages such as surface dressing and also paving in cold weather as a replacement for old 80/100 Penetration grade. The production line of Bitumen Emulsion and Modified Bitumen types can use it. Some kinds of asphalt primer and waterproofing products can be made with Bitumen VG10.
VG 20
VG 20 Bitumen is a standard viscosity grade Bitumen usually used as a paving Bitumen suitable for road construction and other industrial purposes. This grade of bitumen is mainly used for hot mix in moderate climates.
Typical properties of Bitumen VG 20
ABM-Petro group guarantees that the Bitumen Grade VG 20 it supplies under its offers is produced in compliance to and is in conformity to IS 73:2006 and meets the following specification requirements.

Applications
High-altitude regions and cold climates require bitumen VG20 for pavers. It can be used to make some kind of asphalt primer and water-proofing stuff.
VG 30
ABM-Petro group Bitumen Grade VG 30 is a standard viscosity grade Bitumen usually used as a paving material suitable for road construction and other industrial uses.
Bitumen VG-30 is one of the grades in high demand, and it is produced by oxidation of the vacuum bottom in the distillation tower. Hot mix, especially in mild climates, is the main use for this grade of Bitumen.
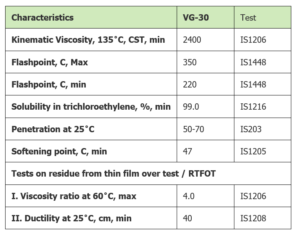
Typical properties of Bitumen VG 30
ABM-Petro group guarantees that the Bitumen Grade VG 30 it supplies under its offers is produced in compliance to and is in conformity to IS 73:2006 and meets the following specification requirements.
Applications
Bitumen VG-30 is used to construct heavy duty pavement projects that must withstand a significant traffic load. VG30 is used extensively in road construction, waterproofing, building construction, and even in the reduction of bitumen production. It can also be used as a replacement for 60/70 Penetration grade. It is the most suitable for use in hot and rainy weather, which can cause many problems in paving, and it is also a good choice for mild regions.
VG 40
ABM-Petro group Bitumen Grade VG 40 is a standard viscosity grade Bitumen usually used as a paving Bitumen suitable for road construction and for the production of superior-quality asphalt surfaces.
Hot mix asphalt for bases and wearing courses is made with this grade of bitumen.
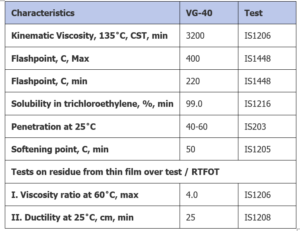
Typical properties of Bitumen VG 40
ABM-Petro group guarantees that the Bitumen Grade VG 40 it supplies under its offers is produced in compliance to and is in conformity to IS 73:2006 and meets the following specification requirements
.
Applications
Truck parking lots, near toll booths and intersections are areas where Bitumen VG-40 is used instead of 30/40 Penetration Grade. Because of the higher viscosity, stiffer Bitumen mixes can be produced in order to improve resistance to shoving and other issues related to heavy traffic loads and higher temperature.
Viscosity grade over penetration grade several key issues are addressed, like:
– Performance at high temperatures by adopting a viscosity-graded bitumen specification (based on viscosity at 60 °C), in place of the current penetration-graded specification (based on penetration at 25 °C)
– Issues relating to compaction, which the tender asphalt mixtures create as push and shove under the roller wheels, have also addressed by having a requirement of minimum viscosity at 135°C, it will be helpful in minimizing the tender mix problems in the field.
– Adoption of viscosity-graded paving bitumen specifications will also reduce the number oftotal tests to 7 without compromising the quality of bitumen and also no new tests are required in implementing this specification.
Viscosity grades Bitumen are categorized according to Viscosity (degree of fluidity) grading. The higher the grade, the stiffer the Bitumen. In Viscosity Grade, Viscosity tests are conducted at 60°C and 135°C, which represents the temperature of road surface during summer and mixing temperature respectively. The penetration at 25°C, which is annual average pavement temperature, has been also retained in Specifications.