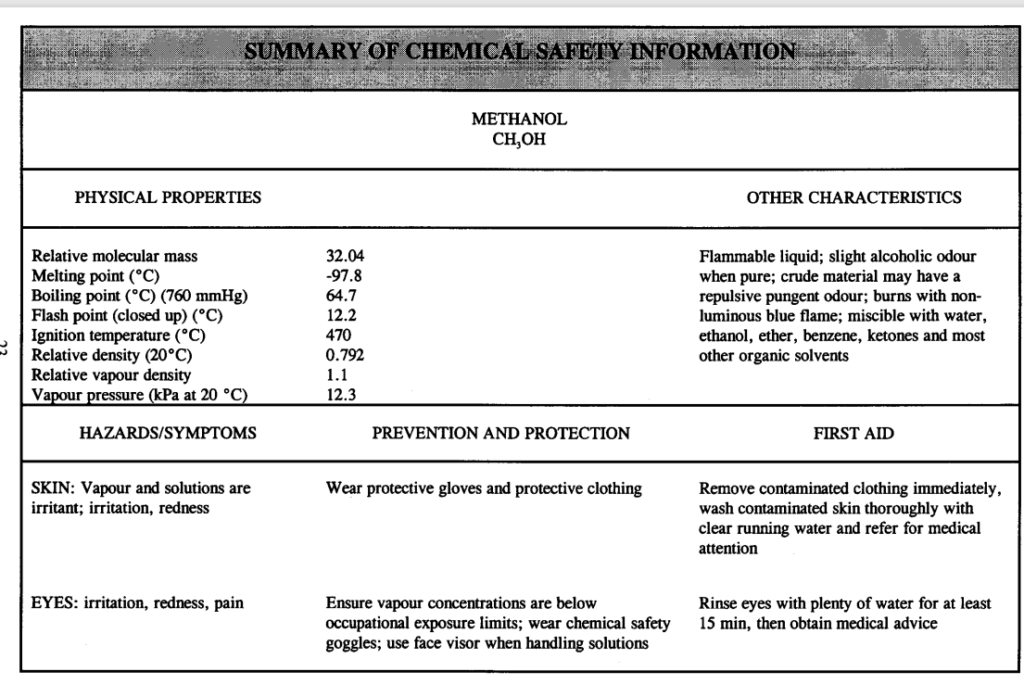
METHANOL
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF METHANOL AS FUEL?
Methanol as a marine fuel has various benefits:
Methanol supply Methanol is a commonly exchanged product regulated by the IBC Code, backed by a robust system of current ports and infrastructure.
Ships can use methanol as fuel without needing cryogenic or high-pressure containment systems due to its liquid state at ambient temperatures.
Advanced engine technology for handling Methanol is well-established, with commercially available two-stroke main engines and four-stroke auxiliary methanol engines.
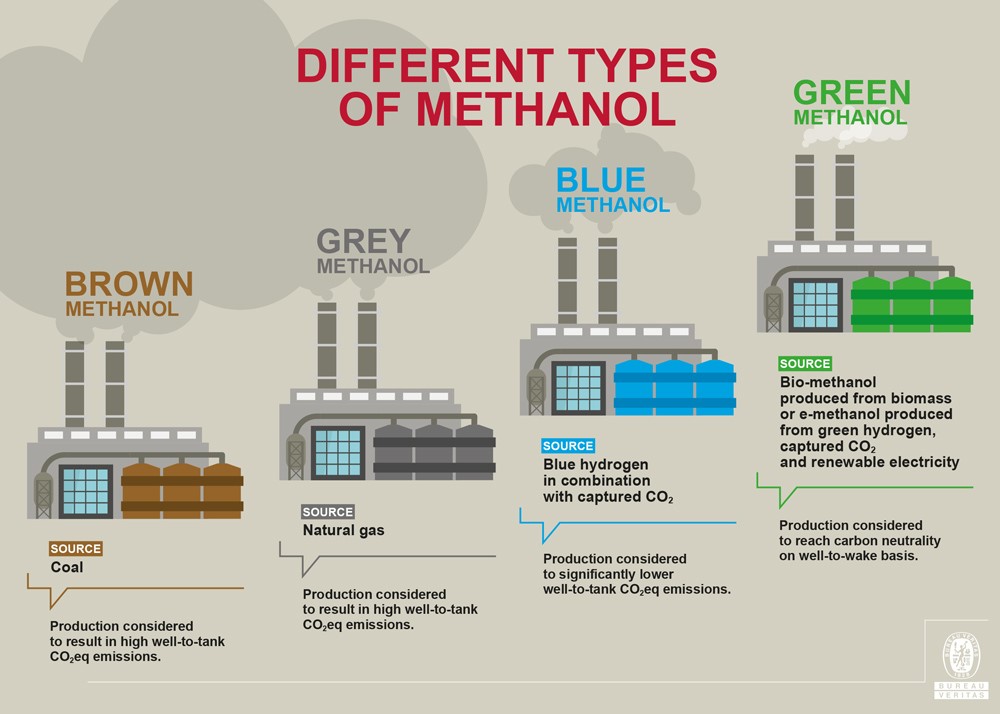
Methanol, which can be produced from renewable energy and carbon capture, has the potential to be a carbon-neutral fuel.
Methanol, or methyl alcohol, is a highly produced chemical globally, with almost 100 million tons manufactured annually from natural gas or coal.
Due to its capability to be stored onboard in liquid form at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure, it provides a solid base for being used as an alternative marine fuel in the shipping industry. Moreover, methanol management and power conversion methods are well-established, and ports already have a solid infrastructure in place. In addition, methanol’s lower levels of pollutants make it a suitable fuel option for individuals aiming to achieve environmental goals.
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET