Rice
Rice is one of the most important cereals and food items in the world. Half of the world’s population relies on rice as a staple food. There are now “tens of thousands of rice” in the world. The traditional method for cultivating rice is flooding the fields while, or after, setting the young seedlings. This simple method requires sound planning and servicing of the water damming and channeling, but reduces the growth of less robust weed and pest plants that have no submerged growth state, and deters vermin. While flooding is not mandatory for the cultivation of rice, all other methods of irrigation require higher effort in weed and pest control during growth periods and a different approach for fertilizing the soil. The products which our company can trade in this field are as follows: Rice 1121 Rice Traditional Basmati Rice PR 11 Rice Swarna Rice Sugandha Rice PR 64 Rice Ponny Rice Sharbati
man
man
Media Paper
LWC This grade of paper is used for publications, advertisements and etc. Art Coated Could be used as packaging and media applications also.
Aluminium
Aluminium is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. It is a silvery-white, soft, non-magnetic and ductile metal in the boron group. By mass, aluminium makes up about 8% of the Earth’s crust; it is the third most abundant element after oxygen and silicon and the most abundant metal in the crust, though it is less common in the mantle below. The chief ore of aluminium is bauxite. Aluminium metal is highly reactive, such that native specimens are rare and limited to extreme reducing environments. Instead, it is found combined in over 270 different minerals.The products which our company can trade in this field are as follows: Aluminum Ingot Aluminum Sows Aluminum Billet Aluminum Rod Aluminum Alloy Alumina
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a blue-silvery appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth’s crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity (electrocuting). The products which our company can trade in this field are as follows: Zinc Ingot 99.95% Zinc Ingot 99.995% Zinc Concentrate Zinc Oxide Zinc Ash Zinc Ore
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is silvery with a hint of blue; it tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively nonreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the group, lead tends to bond with itself; it can form chains and polyhedral structures. The products which our company can trade in this field are as follows : Pure & Refined Lead Ingot Remitted Lead Ingot Antimoney Lead Ingot Lead Ore Lead Concentrate
Polypropylene
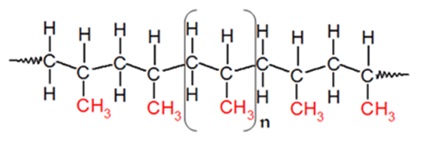
Polypropylene is a tough, rigid and crystalline thermoplastic produced from propene (or propylene) monomer. It is a linear hydrocarbon resin. The chemical formula of polypropylene is (C3H6)n. PP is among the cheapest plastics available today. What is Polypropylene and What It’s Used for? Polypropylene is a tough, rigid and crystalline thermoplastic produced from propene (or propylene) monomer. It is a linear hydrocarbon resin. The chemical formula of polypropylene is (C3H6)n. PP is among the cheapest plastics available today. Molecular Structure of Polypropylene PP belongs to polyolefin family of polymers and is one of the top three widely used polymers today. Polypropylene has applications both as a plastic and a fiber in: Automotive Industry Industrial Applications Consumer Goods, and Furniture Market It has the lowest density among commodity plastics. Some of the key suppliers of polypropylene are: GAPEX, ACCUTECH, POLYFORT, Fiberfil, FERREX and more Daplen, Bormed, Fibremod and more ExxonMobil, Achieve Adstif, Circulen, Hifax, Hostacom, Moplen and more SABIC PP, SABIC Vestolen, LNP THERMOCOMP and more ESD C, ESD A, RTP 100, RTP 101 to 109 and more How to Produce Polypropylene? These days, polypropylene is made from polymerization of propene monomer (an unsaturated organic compound – chemical formula C3H6) by: Ziegler-Natta polymerization or Metallocene catalysis polymerization Upon polymerization, PP can form three basic chain structures depending on the position of the methyl groups: Atactic (aPP) – Irregular methyl group (CH3) arrangement Isotactic (iPP) – Methyl groups (CH3) arranged on one side of the carbon chain Syndiotactic (sPP) – Alternating methyl group (CH3) arrangementWhat is Polypropylene and What It’s Used for?Polypropylene is a tough, rigid and crystalline thermoplastic produced from propene (or propylene) monomer. It is a linear hydrocarbon resin. The chemical formula of polypropylene is (C3H6)n. PP is among the cheapest plastics available today.Molecular Structure of Polypropylene Molecular Structure of Polypropylene PP belongs to polyolefin family of polymers and is one of the top three widely used polymers today. Polypropylene has applications both as a plastic and a fiber in: Automotive Industry Industrial Applications Consumer Goods, and Furniture Market It has the lowest density among commodity plastics. Some of the key suppliers of polypropylene are: A. Schulman – GAPEX®, ACCUTECH™, POLYFORT®, Fiberfil®, FERREX® and more Borealis – Daplen™, Bormed™, Fibremod™ and more ExxonMobil Chemical – ExxonMobil™, Achieve™ LyondellBasell – Adstif, Circulen, Hifax, Hostacom, Moplen and more SABIC – SABIC® PP, SABIC® Vestolen, LNP™ THERMOCOMP™ and more RTP Company – ESD C, ESD A, RTP 100, RTP 101 to 109 and more How to Produce Polypropylene? These days, polypropylene is made from polymerization of propene monomer (an unsaturated organic compound – chemical formula C3H6) by: Ziegler-Natta polymerization or Metallocene catalysis polymerization Structure of PP Monomer Structure of PP Monomer C3H6 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization Arrow Or Metallocene Catalysis Structure of Polypropylene Structure of Polypropylene (C3H6)n Upon polymerization, PP can form three basic chain structures depending on the position of the methyl groups: Atactic (aPP) – Irregular methyl group (CH3) arrangement Isotactic (iPP) – Methyl groups (CH3) arranged on one side of the carbon chain Syndiotactic (sPP) – Alternating methyl group (CH3) arrangement Types of Polypropylene Facts to Know Polypropylene was first polymerized by German chemist named Karl Rehn and an Italian chemist named Giulio Natta to a crystalline isotactic polymer in 1954. This discovery soon led to a large-scale production of polypropylene starting in 1957 by the Italian firm Montecatini. Syndiotactic polypropylene was also first synthesized by Natta and his coworkers. Types of Polypropylene & their Benefits Homopolymers and Copolymers are the two major types of polypropylene available in the market. Polypropylene Homopolymer is the most widely utilized general-purpose grade. It contains only propylene monomer in a semi-crystalline solid form. Main applications include packaging, textiles, healthcare, pipes, automotive and electrical applications. Polypropylene Copolymer family is further divided into random copolymers and block copolymers produced by polymerizing of propene and ethane: Polypropylene Random Copolymer is produced by polymerizing together ethene and propene. It features Ethene units, usually up to 6% by mass, incorporated randomly in the polypropylene chains. These polymers are flexible and optically clear making them suitable of applications requiring transparency and for products requiring an excellent appearance. While in Polypropylene Block Copolymer, ethene content is larger (between 5 and 15%). It has co-monomer units arranged in regular pattern (or blocks). The regular pattern hence makes thermoplastic tougher and less brittle than the random co-polymer. These polymers are suitable for applications requiring high strength, such as industrial usages. Polypropylene, Impact Copolymer – Propylene Homopolymer containing a co-mixed Propylene Random Copolymer phase which has an ethylene content of 45-65% is referred to PP impact copolymer. It is useful in parts which require good impact resistance. Impact copolymers are mainly used in packaging, houseware, film, and pipe applications, as well as in the automotive and electrical segments. Expanded Polypropylene – It is a closed-cell bead foam with ultra-low density. EPP is used to produce three-dimensional polymer foam products. EPP bead foam has higher strength to weight ratio, excellent impact resistance, thermal insulation, and chemical and water resistance. EPP is used in various applications ranging from automobiles to packaging, from construction products to consumer goods and more. Polypropylene Terpolymer – It is composed by propylene segments joined by monomers ethylene and butane (co-monomer) which appear randomly throughout the polymer chain. PP terpolymer has better transparency than PP homo. Also, the incorporation of co-monomers reduces crystalline uniformity in the polymer making it suitable for sealing film applications. Polypropylene, High Melt Strength (HMS PP)– It is a long chain branched material, which combines both high melt strength and extensibility in the melt phase. PP HMS grades have a wide mechanical property range, high heat stability, good chemical resistance. HMS PP is widely used to produce soft, low density foams for food packaging applications as well as used in automotive and construction industries.